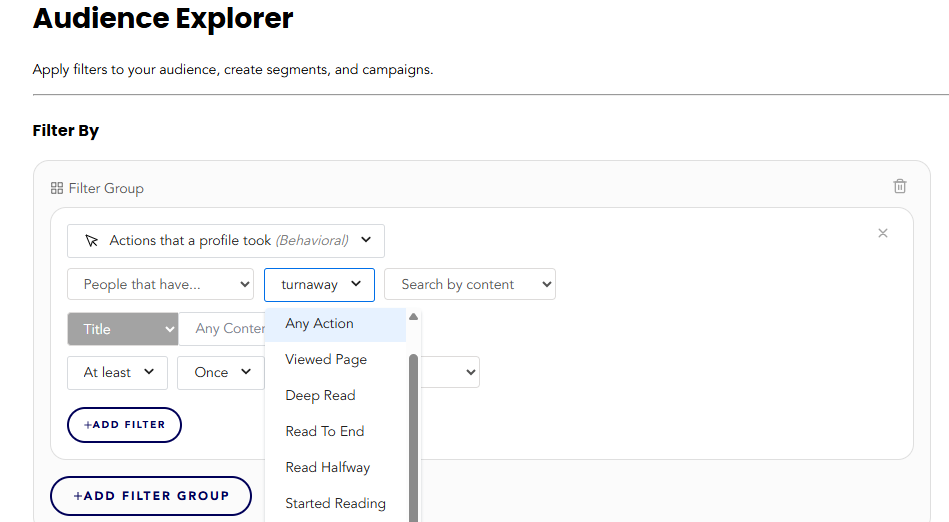
- Viewed Article
The user clicked on an article but may not have actively engaged with the content (e.g., skimming or exiting quickly). This is typically tracked as a “pageview” or similar action. - Started Reading
The user scrolled past the initial part of the page, indicating they began engaging with the content beyond just opening it. This is often measured by scrolling a certain percentage of the page or spending a minimum amount of time on it. - Read Halfway
The user scrolled or interacted with at least 50% of the article, suggesting moderate engagement. - Read to End
The user reached the bottom of the article, indicating they consumed the content in full. Sometimes, time spent on the page is also factored in to ensure it matches the content length. - Deep Read
The user not only reached the end of the article but also demonstrated deeperengagement. This could involve spending more time on the page, scrolling back to reread sections, or interacting with elements like links, multimedia, or comments.
You might notice that some of these metrics, such as “Deep Read,” don’t rely solely on time-based measurement. There’s a time component, but it’s more nuanced than the standard “time on page” metrics that other systems track. Instead, we look at behaviors like scrolling patterns. For instance, we can detect when someone is scrolling quickly versus engaging deeply. Those behaviors are baked into the behavioral events described above.
For “Deep Read,” specifically, it combines multiple actions: a page view, starting to read, reaching halfway, and finishing the article. The system uses the beacon to measure the length of the page and break it into sections, which helps us track these engagement levels accurately.